The Sumitomo Rubber Group has established a fundamental risk management policy of eliminating and mitigating risks that could significantly impact stable business activities and compliance with laws and regulations, to promote the realization of Our Philosophy.
Management risks involving product quality, the law, the environment, credit, accidents, disasters, etc., that may materially and adversely affect our business activities, shall be addressed by the relevant division and/or subsidiary in advance, through the analysis of those risks and the planning of countermeasures in accordance with the Regulations Concerning Risk Control, which define risk management methods for the entire Our Group. These risks shall be then referred to the Management Meeting and other bodies for discussion. If necessary, advice and guidance may be sought from professionals, including legal counsel, in analyzing and planning countermeasures for such risks.
Our Group undertakes the periodic review of risks in light of changes in risks associated with and the external environment surrounding its business operations. We evaluate risks based on a five-point scale for the impact and frequency of occurrence. In assessing the impact, we conduct a quantitative evaluation from five perspectives: monetary damages, human loss, environmental impact, damage to social reputation, and impact on research and development, manufacturing, and sales activities. We define priority risks that could cause significant damage to the Group’s business and prioritize them as requiring an immediate response.
●Risks associated with natural disasters
●Risks associated with information security
●Risks associated with occupational accidents, fires, etc.
●Risks associated with sustainability management
●Risks associated with product quality management
●Risks associated with human rights violations
●Risks associated with the political situation and economic trends, etc.
●Risks associated with human resource acquisition
●Risks associated with compliance
●Risks associated with intellectual properties
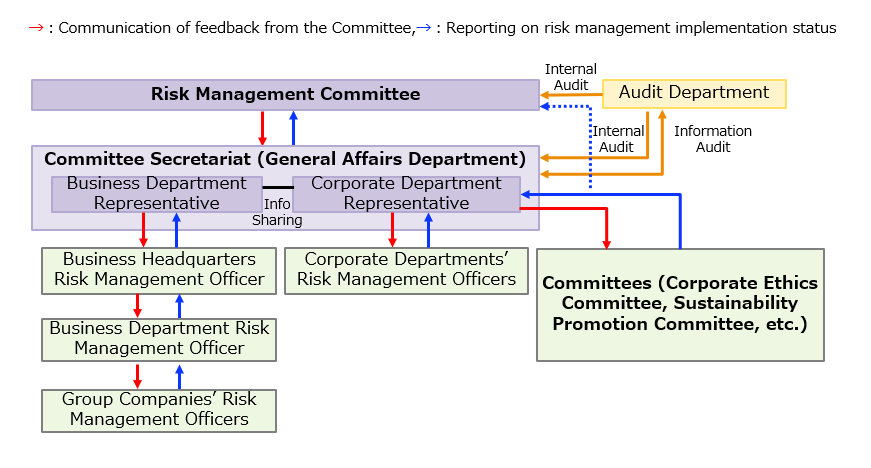
Our group has established a company-wide risk management framework centered on the Risk Management Committee, referencing ISO 31000. An overview is shown in the diagram below.
The Risk Management Committee identifies and evaluates priority risks that could hinder the execution of the medium-term management plan and the achievement of objectives. It deliberates on activity policies for risk management, responses to risks requiring company-wide action due to risk fluctuations, and other important matters related to company-wide risk management. It also monitors the status of responses to priority risks by each department and group company. These efforts are reported to the Board of Directors, which monitors them to confirm the effectiveness of risk management.
Furthermore, each department and group company appoints a risk management officer to manage the risks specific to their organization. This structure enables the appropriate management of risks by detecting and analyzing the diversifying and complexifying risks within the constantly changing social and business environment for each business division.
Having directly experienced fallout from the Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake and the Great East Japan Earthquake, Our Group has developed BCPs by drawing on takeaways from these two major earthquakes. Specifically, we completed the formulation of well-thought-out BCPs encompassing our Head Office, overseas and Japan-based factories and domestic subsidiaries to protect human life as well as to facilitate the early resumption of product deliveries to customers at times of emergency. We also conduct periodic drills to enhance the effectiveness of these BCPs. We also upgraded the BCPs to be executed in the case of war. This upgrade was informed by fresh discussions regarding how to secure the safety of expatriates and local employees at times of emergency and how to continue sales, logistics, raw material procurement, and other essential activities, drawing on takeaways from our response to past incidents.
We conduct scenario analysis using multiple scenarios for representative climate change risks among sustainability issues that could significantly impact business activities. For details, please refer to “Information disclosure aligned with the TCFD and TNFD recommendations.”
The targets and results are as follows.
| 2025 targets |
|
|---|---|
| 2025 results |
|
| 2026 targets |
|
| Medium-to long-term targets |
|
In fiscal year 2025, we promoted the formalization of revised risk management regulations and the restructuring of a group-wide risk management framework. We worked to strengthen collaboration within each business division and enhance the effectiveness of group-wide risk management. In fiscal year 2026, we will conduct a company-wide risk analysis survey and review the company's priority response risks.
In fiscal 2025, considering the global nature of the Company’s business activities, the Risk Management Committee confirmed that the management system was functioning effectively based on reports from the departments in charge regarding the following risks.
Examples of reports:
1.Compliance-related risks
2.Risks related to the procurement of raw materials
3.Risks related to information security, such as cyber attacks
Aware of the growing magnitude of the threats of typhoons, heavy rains, and other natural disasters that have been striking the country in recent years, we have upgraded the content of BCPs by incorporating lessons learned in the course of disaster responses. For example, in fiscal 2019 we established standards for exempting employees from attendance at or allowing them to leave early from their workplaces when public transportation is disrupted by an earthquake or when evacuation is instructed by government agencies due to heavy rains or flooding. We have also provided employees with a renewed version of the Basics of What to Do When a Disaster Strikes handbook, which incorporates the above standards to ensure robust employee understanding of these matters. We conduct regular earthquake evacuation and safety confirmation drills to improve our initial response to disasters and raise employee awareness of disaster prevention. Looking ahead, we will develop a more robust structure capable of keeping our BCPs up-to-date from the perspectives of ensuring the safety of employees and securing business continuity.

“Basics of What to Do When a Disaster Strikes” portable card